 04-链表问题
04-链表问题
# 在节点间穿针引线(反转链表)
# 题目分析
206. 反转链表 (opens new window)简单
给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
通常情况下链表问题我们是不能操作节点中值的,应该操作节点的指向,即实现如下图操作。
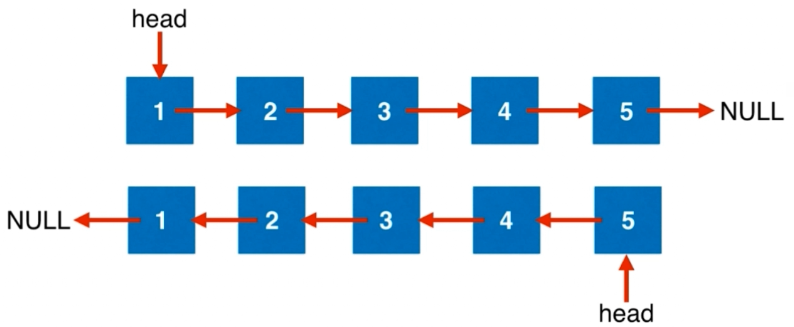
在遍历链表时,将当前节点的 next 指针改为指向前一个节点。由于节点没有引用其前一个节点,因此必须事先存储其前一个节点。在更改引用之前,还需要存储后一个节点。最后返回新的头引用。整体过程如下图。
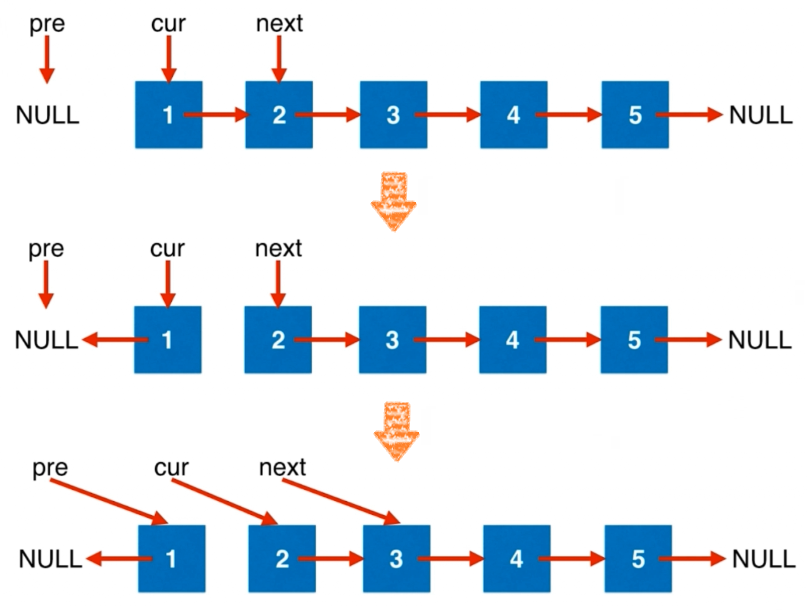
# 代码实现
迭代法
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } * 迭代法 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode cur = head; // 保存当前遍历的节点 ListNode pre = null; // 保存前一个节点 while (cur != null) { ListNode next = cur.next; // 暂存下一个节点 cur.next = pre; // 指针反转 // 操作完成,pre 和 cur 后移动一位,继续 pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28递归法。递归法比较难懂,借助 LeetCode 解题理解。
/** * 递归 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next); // newHead 始终是原链表的尾节点 head.next.next = head; // 将下一节点的 next 指向自己,形成环 head.next = null; // 保留反转后的指向,取消原指向,解开环 return newHead; // 返回原链表的尾节点 } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 相关问题
92. 反转链表 II (opens new window)中等
给你单链表的头指针
head和两个整数left和right,其中left <= right。请你反转从位置left到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
截取拼接子链表,两次遍历。
/** * 两次遍历迭代法,截取拼接 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) { // 因为头节点可能参与反转,设置虚拟头节点可以避免复杂的分类讨论 ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); dummyHead.next = head; // 从虚拟头节点走 left - 1 步,定位到子链表前驱节点 ListNode pre = dummyHead; for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) { pre = pre.next; } // 从 pre 再走 right - left + 1 步,定位到子链表 right 节点 ListNode rightNode = pre; for (int i = 0; i < right - left + 1; i++) { rightNode = rightNode.next; } // 定位子链表 left 节点和后继节点 succ ListNode leftNode = pre.next; ListNode succ = rightNode.next; // 截断子链表 pre.next = null; rightNode.next = null; // 反转子链表 reverseList(leftNode); // 将子链表拼接回去 pre.next = rightNode; leftNode.next = succ; return dummyHead.next; } // 完整反转链表方法,也可以使用递归 private void reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode cur = head; ListNode pre = null; while (cur != null) { ListNode nextNode = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = nextNode; } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53头插法。一次遍历,且步骤简洁。思路参考:Java-双指针-头插法 (opens new window)
/** * 头插法 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) { // 因为头节点可能参与反转,设置虚拟头节点可以避免复杂的分类讨论 ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); dummyHead.next = head; // 定位子区间的前驱节点 pre 和区间起点 leftNode ListNode pre = dummyHead; for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) { pre = pre.next; } ListNode leftNode = pre.next; // 循环将 leftNode 右边的头插到 pre 后面,结束后 leftNode 来到子区间右边 for (int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) { // 移除后面一个节点,摘出来 ListNode removeNode = leftNode.next; leftNode.next = leftNode.next.next; // 将摘出来的节点拼到 pre 后面 removeNode.next = pre.next; pre.next = removeNode; } return dummyHead.next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 (opens new window)简单
存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点
head,请你删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 。返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。
/**
* 一次遍历
* 时间复杂度: O(N)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return head;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == cur.val)
cur.next = cur.next.next;
else
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
给你一个链表的头节点
head和一个特定值x,请你对链表进行分隔,使得所有 小于x的节点都出现在 大于或等于x的节点之前。你应当 保留 两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
分成两个链表,再拼接。
/** * 分组拼接 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) { // 分成大链表和小链表 ListNode smallHead = new ListNode(0); // 小链表头(虚拟) ListNode smallTail = smallHead; // 小链表尾 ListNode largeHead = new ListNode(0); // 大链表头(虚拟) ListNode largeTail = largeHead; // 大链表尾 // 遍历节点,将元素划分到两个链表中 while (head != null) { if (head.val < x) { smallTail.next = head; smallTail = smallTail.next; } else { largeTail.next = head; largeTail = largeTail.next; } head = head.next; } // 其 next 指针可能指向一个小于 x 的节点,所以要置空 largeTail.next = null; smallTail.next = largeHead.next; // 拼接两个链表 return smallHead.next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31快速排序 partition 思想。
/** * 快速排序 partition 操作思想 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) { if (head == null) return head; // 设置虚拟头节点 ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); dummyHead.next = head; // 先跳过初始链表前面所有小于 x 的节点,使得 limit 指向左侧小于 x 区间的最后一个节点 ListNode limit = dummyHead; // 分界点 while (limit.next != null && limit.next.val < x) limit = limit.next; // 开始遍历节点,pre 指向待考察节点的前一个节点 ListNode pre = limit; while (pre.next != null) { if (pre.next.val < x) { // 如果下一个节点小于 x // 移除下一个节点 removeNode ListNode removeNode = pre.next; pre.next = pre.next.next; // 将 removeNode 拼到前面小于 x 区间的后面 removeNode.next = limit.next; limit.next = removeNode; // 更新分界点 limit = removeNode; } else { pre = pre.next; // 不小于 x 的直接跳过 } } return dummyHead.next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
328. 奇偶链表 (opens new window)中等
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
请尝试使用原地算法完成。你的算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时间复杂度应为 O(nodes),nodes 为节点总数。
分组合并。官方解法。
/** * 分离节点后合并 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) { if (head == null) return head; ListNode evenHead = head.next; // 偶串头节点 ListNode odd = head, even = evenHead; // 奇、偶串尾节点 // 等于一次移动两个节点 while (even != null && even.next != null) { // 更新奇串尾部 odd.next = even.next; odd = odd.next; // 更新偶串尾部 even.next = odd.next; even = even.next; } odd.next = evenHead; // 拼接奇偶串 return head; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23partition 思想。
/** * 遍历,partition 思想 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution2 { public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) { if (head == null) return head; // 分界点,奇区的最后一个节点 ListNode lastOdd = head; // 待考察节点的前驱节点,是一个偶节点,也是已经排好的最后一个偶节点 ListNode lastEven = head.next; while (lastEven != null && lastEven.next != null) { // 移除下一个节点 removeNode,是一个奇节点 ListNode odd = lastEven.next; lastEven.next = lastEven.next.next; // 将 removeNode 拼到前面小于 x 区间的后面 odd.next = lastOdd.next; lastOdd.next = odd; // 更新标记点 lastOdd = odd; lastEven = lastEven.next; } return head; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
/**
* 同时遍历两个链表
* 时间复杂度: O(max(m,n)) 其中 m、n 分别表示 l1、l2 节点数
* 空间复杂度: O(1) 官方说返回值不计入空间复杂度
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = null, tail = null; // 返回链表的头和尾
int carry = 0; // 进位值
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
// 计算当前数位的和 sum
int val1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
int val2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
int sum = val1 + val2 + carry; // 加上上一次的进位
// 创建节点,接到尾部
ListNode node = new ListNode(sum % 10);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
tail = node;
} else {
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
}
// 记录进位值
carry = sum / 10;
// l1、l2 指向下一个
if (l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;
if (l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;
}
// 不要忘记考虑最后还有进位的情况
if (carry > 0) tail.next = new ListNode(carry);
return head;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
445. 两数相加 II (opens new window)中等
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
/**
* 栈
* 时间复杂度: O(max(m,n)) 其中 m 和 n 分别为两个链表的长度
* 空间复杂度: O(m+n)
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null) {
s1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
s2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0; // 进位值
ListNode curNode = null;
while (!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty() || carry > 0) {
int a = s1.isEmpty() ? 0 : s1.pop();
int b = s2.isEmpty() ? 0 : s2.pop();
int cur = a + b + carry;
carry = cur / 10;
cur %= 10;
curNode = new ListNode(cur, curNode);
}
return curNode;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 设立链表的虚拟头结点(移除链表元素)
# 题目分析
203. 移除链表元素 (opens new window)简单
给你一个链表的头节点
head和一个整数val,请你删除链表中所有满足Node.val == val的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
要删除一个元素应该怎么做呢?我们在遍历链表过程中,如果发现当前节点 cur 的下一个节点就是待删除的节点 delNode,我们就执行 cur.next = delNode.next 就可以直接跳过待删除节点(可选操作:释放 delNode 空间),如下图所示。
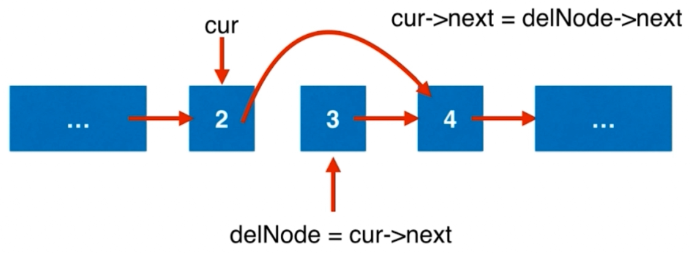
这个操作对 delNode 是最后一个元素同样适用。但是这样的操作对 delNode 是第一个元素是不适用的,因为这套操作的 cur 是 delNode 的前一个节点,如果 delNode == head,则 delNode 的前面没有任何元素。对此,我们需要对头节点进行单独操作。
# 代码实现
迭代法,不设置虚拟头节点。
/** * 迭代法 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { // 删除链表开头所有符合条件的节点 while (head != null && head.val == val) head = head.next; if (head == null) return head; // 开始逐个考察节点,删除中间的节点 ListNode cur = head; while (cur.next != null) { if (cur.next.val == val) { cur.next = cur.next.next; // 跨过待删除节点 } else { cur = cur.next; } } return head; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26迭代法,设置虚拟头节点。
/** * 迭代法,设置虚拟头节点 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { // 设置虚拟头节点 ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead.next = head; // 开始逐个考察节点,删除中间的节点 ListNode cur = dummyHead; while (cur.next != null) { if (cur.next.val == val) { cur.next = cur.next.next; // 跨过待删除节点 } else { cur = cur.next; } } return dummyHead.next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24递归法
/** * 递归法 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution2 { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { if (head == null) return head; ListNode node = removeElements(head.next, val); if (head.val == val) head = node; else head.next = node; return head; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 相关问题
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II (opens new window)中等
存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点
head,请你删除链表中所有存在数字重复情况的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字。返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。
/**
* 一次迭代
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = dummyHead;
while (pre.next != null && pre.next.next != null) {
if (pre.next.val == pre.next.next.val) {
int x = pre.next.val; // 重复值
while (pre.next != null && pre.next.val == x) {
pre.next = pre.next.next; // 删除所有重复值节点
}
} else {
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
21. 合并两个有序链表 (opens new window)简单
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
迭代法
/** * 迭代法 * 时间复杂度: O(m+n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); // 归并操作 ListNode pre = dummyHead; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val < l2.val) { pre.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } else { pre.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } pre = pre.next; } // 将归并完的部分拼上 pre.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1; return dummyHead.next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27递归法
/** * 递归法: 两个链表头部值较小的一个节点与剩下元素的 merge 操作结果合并。 * 时间复杂度: O(m+n) * 空间复杂度: O(m+n) */ class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { if (l1 == null) { return l2; } else if (l2 == null) { return l1; } else if (l1.val < l2.val) { l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2); return l1; } else { l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next); return l2; } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 复杂的穿针引线(两两交换链表中的节点)
# 问题分析
24. 两两交换链表中的节点 (opens new window)简单
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]1
2
如下图,交换每一对元素,以 (1,2) 为例,交换完位置后,应该让 pre(1) -> 2 -> 1 -> next(2),其中 pre(1) 表示 1 的前一个节点,next(2) 表示 2 的后一个节点。过程中我们需要知道 pre(1) 是谁,但是头节点 head 没有前一个节点。这种情况下我们又要对头节点作特殊处理,为了避免这种特殊处理我们需要设置虚拟头节点。
在设置了虚拟头节点后,我们需要将 pre(1) -> 2,所以我们设置一个指针 p 表示需要交换的一对节点之前的一个节点。另外还需要两个指针指向待交换的两个节点 node1、node2,此外还需要让 1 -> next(2),所以还需要一个指针 next 指向待交换的两个节点的下一个节点。
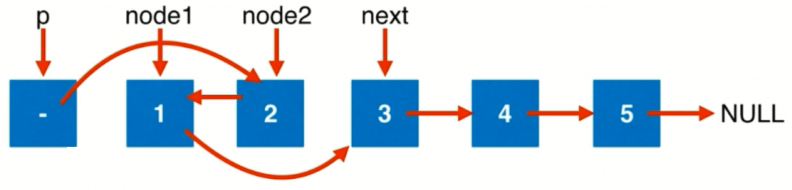
有了这 4 个指针,我们只需要执行如下操作即可。
node2.next = node1; // node2 指向 node1
node1.next = next; // node1 执行后续节点
p.next = node2; // 前节点指向 node2
2
3
此时这一对节点就完成交换了,此时我们还需要将 p 指针指向 node1,也就是下一对待交换节点之前的节点,然后根据 p 重新定义 node1、node2 和 next,重复上述操作即可。
# 代码实现
迭代
/** * 迭代法 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { // 设置虚拟头节点 ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead.next = head; ListNode p = dummyHead; // pre 指向待交换节点的前一个节点 while (p.next != null && p.next.next != null) { // 记录要交换的两个节点和后续节点 ListNode node1 = p.next; ListNode node2 = node1.next; ListNode next = node2.next; // 进行交换操作 node2.next = node1; node1.next = next; p.next = node2; // 更新 pre p = node1; } return dummyHead.next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28递归
/** * 递归法 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution2 { public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; // 每次递归跳过两个节点 ListNode subList = swapPairs(head.next.next); ListNode next = head.next; next.next = head; head.next = subList; return next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 相关问题
25. K 个一组翻转链表 (opens new window)困难
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
/**
* 遍历,分段
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = dummyHead;
while (pre.next != null) {
ListNode segHead = pre.next; // 分段头
ListNode segTail = pre; // 分段尾
// 判断是否还够一段
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
segTail = segTail.next;
if (segTail == null) // 如果不够一段,直接返回
return dummyHead.next;
}
ListNode next = segTail.next; // 下一段开头
// 断开本段
pre.next = null;
segTail.next = null;
// 反转本段
this.reverse(segHead);
// 拼接本段
pre.next = segTail;
segHead.next = next;
// 更新 pre
pre = segHead;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
// 反转链表
private void reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
147. 对链表进行插入排序 (opens new window)中等
对链表进行插入排序。
插入排序的动画演示如上。从第一个元素开始,该链表可以被认为已经部分排序(用黑色表示)。 每次迭代时,从输入数据中移除一个元素(用红色表示),并原地将其插入到已排好序的链表中。
/**
* 时间复杂度: O(n^2)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode lastSorted = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val >= lastSorted.val) {
lastSorted = lastSorted.next;
} else {
ListNode pre = dummyHead;
while (pre.next.val < cur.val) {
pre = pre.next;
}
lastSorted.next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre.next;
pre.next = cur;
}
cur = lastSorted.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
148. 排序链表 (opens new window)中等
给你链表的头结点
head,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
归并排序,自顶向下
/** * 自顶向下归并排序,递归法 * 时间复杂度: O(NlogN) * 空间复杂度: O(logN) */ class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; // 快慢指针寻找链表中点 ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; while (true) { fast = fast.next; if (fast == null || fast.next == null) break; fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } ListNode mid = slow; // 链表中点,l1 的尾节点 ListNode head2 = mid.next; // l2 的头节点 mid.next = null; // 断开 l1 和 l2 // 排序归并两个链表 ListNode l1 = sortList(head); ListNode l2 = sortList(head2); return merge(l1, l2); } // 归并链表 private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); ListNode tail = dummyHead; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val < l2.val) { tail.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } else { tail.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } tail = tail.next; } if (l1 == null) tail.next = l2; if (l2 == null) tail.next = l1; return dummyHead.next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53归并排序,自底向上
/** * 归并排序,自底向上 * 时间复杂度: O(NlogN) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; // 统计链表长度 int length = 0; ListNode node = head; while (node != null) { length++; node = node.next; } ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head); for (int subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength *= 2) { ListNode pre = dummyHead; // 前面已经完成归并的尾节点 ListNode cur = dummyHead.next; // 待归并部分的首节点 while (cur != null) { // 找到长度为 subLength 的小段 l1 ListNode l1 = cur; for (int i = 1; i < subLength && cur.next != null; i++) cur = cur.next; // 找到长度为 subLength 的小段 l2 ListNode l2 = cur.next; cur.next = null; // 截断 l1 cur = l2; for (int i = 1; i < subLength && cur != null && cur.next != null; i++) cur = cur.next; ListNode next = null; if (cur != null) { next = cur.next; cur.next = null; // 截断 l2(如果后面的话) } cur = next; // 归并 l1 和 l2,拼接到 pre 上 pre.next = merge(l1, l2); // 更新 pre while (pre.next != null) { pre = pre.next; } } } return dummyHead.next; } // 归并链表 private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); ListNode tail = dummyHead; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val < l2.val) { tail.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } else { tail.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } tail = tail.next; } if (l1 == null) tail.next = l2; if (l2 == null) tail.next = l1; return dummyHead.next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
# 不仅仅是穿针引线(删除链表中的节点)
之前我们介绍的链表问题都是在链表中穿针引线,不过有时候我们的思路要灵活些,有的链表问题不仅仅是穿针引线。
237. 删除链表中的节点 (opens new window)简单
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点。传入函数的唯一参数为 要被删除的节点 。
这个问题和之前一个删除节点的问题很相似,但是要注意的是这个问题的传入参数是 要被删除的节点,并不是头节点和待删除节点。如下图,如果要删除节点 3,函数入参只有节点 3,我们拿不到 3 的前一个节点。
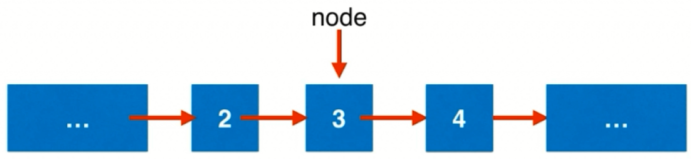
之前我们说过一般不能操作节点中的 val,但是这个问题只能这么作。我们把节点 4 的值赋给 3,然后 node.next = node.next.next 跨过原节点 4 即可。
/**
* 时间复杂度: O(1)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
if (node == null || node.next == null) {
node = null;
return;
}
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 链表与双指针(删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点)
# 问题分析
我们曾经在研究数组问题的时候介绍过双指针技术,链表中有时候也可以通过定义双指针解决问题。
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 (opens new window)中等
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第
n个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
计算链表长度
先遍历一遍计算链表长度 l,再遍历一遍删除倒数第 n 个节点,即正数第 l-n 个节点。
/** * 计算链表长度 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution2 { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head); // 计算链表长度 int length = 0; for (ListNode cur = dummyHead.next; cur != null; cur = cur.next) length++; // 计算待删除元素是整数第几个 int k = length - n; ListNode cur = dummyHead; for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) cur = cur.next; // 删除元素 cur.next = cur.next.next; return head; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23虚拟头节点 + 滑动窗口
解法2:如下图所示,设置虚拟头节点,然后定义一个窗口 [p,q],初始 p 指向虚拟头节点,q 和 p 中间隔 n 个节点,即 q 指向 p 经过 n+1 次 next 后指向的节点。然后 p、q 同事右移直到 q 到了 null 位置,此时 p 就指向待删除节点的前一个节点了。
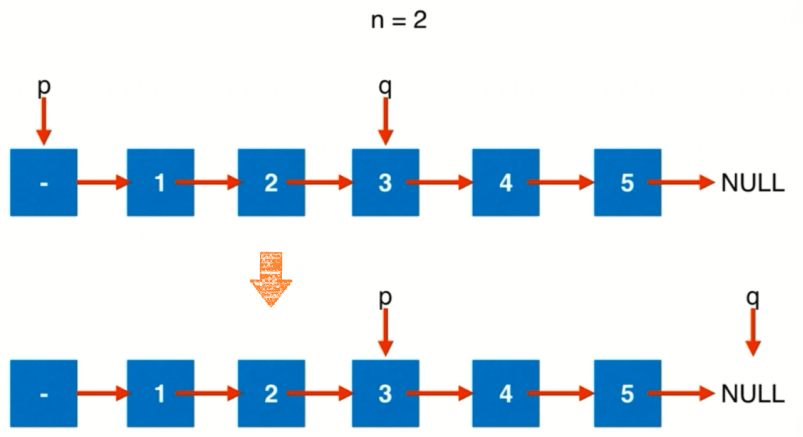
/** * 虚拟头节点 + 滑动窗口 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, head); // 初始化双指针,确定滑动窗口 ListNode l = dummyHead, r = dummyHead; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) r = r.next; // 窗口右滑至末尾 while (r.next != null) { l = l.next; r = r.next; } // 删除节点 l.next = l.next.next; return dummyHead.next; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 相关问题
给你一个链表的头节点
head,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动k个位置。
/**
* 两次遍历,闭合成环再解开
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (k == 0 || head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
// 统计长度
int length = 1;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
length++;
}
// 计算实际需要移动的步数
int step = length - k % length;
if (step == length)
return head;
// 先成环,cur 指向原 head 前一个节点
cur.next = head;
for (int i = 0; i < step; i++)
cur = cur.next;
// 解开环
ListNode newHead = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
return newHead;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
143. 重排链表 (opens new window)中等
给定一个单链表
L的头节点head,单链表L表示为:L0 → L1 → … → Ln-1 → Ln请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln-1 → L2 → Ln-2 → …不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
/**
* 寻找链表中点 + 链表后半部逆序 + 合并链表
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return;
// 寻找链表中点
ListNode mid = middleNode(head);
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
// 链表逆序
l2 = reverseList(l2);
// 合并链表
mergeList(l1, l2);
}
// 快慢指针寻找链表中点
private ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 链表反转
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
// 合并链表
private void mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
// 两个链表的下一链表
ListNode next1 = l1.next;
ListNode next2 = l2.next;
// 合并连接链表
l1.next = l2;
l2.next = next1;
// 更新 l1、l2
l1 = next1;
l2 = next2;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
234. 回文链表 (opens new window)中等
给你一个单链表的头节点
head,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回true;否则,返回false。**进阶:**你能否用
O(n)时间复杂度和O(1)空间复杂度解决此题?
/**
* 寻找链表中点 + 链表后半部逆序 + 对比链表
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return true;
// 找中点
ListNode mid = middleNode(head);
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
// 反转后半部
l2 = reverseList(l2);
// 对比链表
return compareList(l1, l2);
}
// 快慢指针寻找链表中点
private ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 链表反转
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
// 对比两个链表
private boolean compareList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val != l2.val)
return false;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
return true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
