 03-迭代器与循环
03-迭代器与循环
# Iterator
以数组为例:
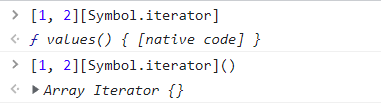
const it = [1, 2][Symbol.iterator]();
console.log(it);
1
2
2
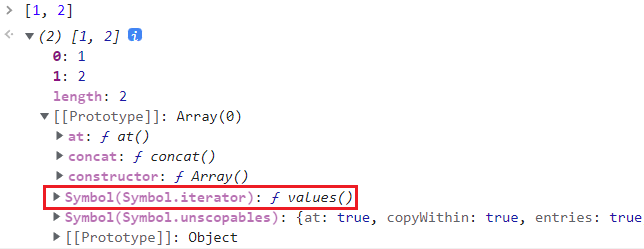
其中 it 就是可迭代对象,Symbol.iterator 是可迭代对象的生成方法。
使用 Iterator
const it = [1, 2][Symbol.iterator]();
console.log(it.next()); // {value: 1, done: false}
console.log(it.next()); // {value: 2, done: false}
console.log(it.next()); // {value: undefined, done: true}
console.log(it.next()); // {value: undefined, done: true}
// 使用 Iterator 遍历
const it2 = [1, 2][Symbol.iterator]();
let next = it2.next();
while (!next.done) {
console.log(next.value);
next = it2.next();
console.log(next);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Symbol.iterator(可迭代对象的生成方法)-> it(可迭代对象) -> it.next() -> it.next() -> ...(直到 done 为 true)。
已知的遍历方式:
- 遍历数组:for 循环和 forEach 方法
- 遍历对象:for in 循环
那为什么还需要 Iterator 呢?
Iterator 遍历器是一个统一的遍历的机制 Symbol.iterator -> it -> next() 。对于数组天生可以使用 Iterator,对于对象我们也可以实现一个 Symbol.iterator 方法来获取可迭代对象,用来遍历。
但是其实我们一般不直接使用 Iterator 去遍历,而是使用封装好的方式,比如 for...of。
# for...of
for...of 就是对 Iterator 遍历流程的封装。
for (const item of arr) {
console.log(item);
}
1
2
3
2
3
for...of 遍历中如何得到索引值呢?下面介绍三个方法:keys()、values()、entries()。
keys() 得到的是索引的可遍历对象,可以遍历出索引值。
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
for (const key of arr.keys()) {
console.log(key);
}
// 遍历出 0 1 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
values() 得到的是值的可遍历对象,可以遍历出值。
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
for (const value of arr.values()) {
console.log(value);
}
// 和直接使用 for...of 结果相同,遍历出 1 2 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
entries() 得到的是索引和值组成的数组的可遍历对象。
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
for (const entry of arr.entries()) {
//console.log(entry); // 两个元素的数组 [索引, 元素]
console.log(`索引是${entry[0]},元素是${entry[1]}`)
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# 原生可遍历与非原生可遍历
什么是可遍历?
只要有 Symbol.iterator 方法,并且这个方法可以生成可遍历对象,就是可遍历的。只要可遍历,就可以使用 for...of 循环来统一遍历。
原生可遍历的有哪些?
- 数组
- 字符串
- Set
- Map
- arguments
- NodeList
非原生可遍历的有哪些?
- 一般的对象
除非自己实现 Symbol.iterator 方法。
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2023/06/04, 12:34:19
