06-二叉树和递归
06-二叉树和递归
# 二叉树天然的递归结构(二叉树的最大深度)
# 问题分析
二叉树是天然的递归结构,它的左子树也是二叉树,右子树也是二叉树,并且没有递归终止条件,并且空也是二叉树。
104. 二叉树的最大深度 (opens new window)简单
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
深度优先遍历(递归)
/** * 深度优先遍历(递归) * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(height) */ class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12广度优先遍历(队列)
/** * 广度优先遍历(队列) * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: 取决于队列中存储的元素,最坏 O(n) */ class Solution2 { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); int depth = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left); if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right); } depth++; } return depth; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 相关问题
111. 二叉树的最小深度 (opens new window)简单
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
深度优先遍历
/** * 深度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(H),平均情况下为 O(logN) */ class Solution { public int minDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else if (root.left == null) { return minDepth(root.right) + 1; } else if (root.right == null) { return minDepth(root.left) + 1; } else { return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1; } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18广度优先遍历
/** * 广度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(N) */ class Solution { public int minDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); int minDepth = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { return minDepth + 1; } if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left); if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right); } minDepth++; } return 0; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 一个简单的二叉树问题引发的血案(翻转二叉树)
# 问题分析
226. 翻转二叉树 (opens new window)简单
翻转一棵二叉树。
/**
* 递归翻转二叉树
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
* 空间复杂度: O(n)
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return root;
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 相关问题
100. 相同的树 (opens new window)简单
给你两棵二叉树的根节点
p和q,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
深度优先搜索
/** * 深度优先搜索 * 时间复杂度: O(min(m, n)), 其中 m 和 n 分别是两个二叉树的节点数。 * 空间复杂度: O(min(m, n)) */ class Solution { public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (p == null && q == null) { return true; } else if (p == null || q == null || p.val != q.val) { return false; } else { return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16广度优先搜索
/** * 广度优先搜索 * 时间复杂度: O(min(m, n)), 其中 m 和 n 分别是两个二叉树的节点数。 * 空间复杂度: O(min(m, n)) */ class Solution { public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (p == null && q == null) return true; else if (p == null || q == null || p.val != q.val) return false; Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<>(); Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<>(); queue1.offer(p); queue2.offer(q); while (!queue1.isEmpty() || !queue2.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node1 = queue1.poll(); TreeNode node2 = queue2.poll(); if (node1.val != node2.val) return false; TreeNode left1 = node1.left, left2 = node2.left, right1 = node1.right, right2 = node2.right; // 异或运算,判断空值情况 if (left1 == null ^ left2 == null || right1 == null ^ right2 == null) return false; if (left1 != null) { queue1.offer(left1); queue2.offer(left2); // 经过异或判断,left2 != null 也成立 } if (right2 != null) { queue1.offer(right1); queue2.offer(right2); // 经过异或判断,right2 != null 也成立 } } return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty(); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
101. 对称二叉树 (opens new window)简单
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
递归
/** * 递归 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { return check(root, root); } private boolean check(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (p == null && q == null) return true; // 同时为空 true else if (p == null || q == null) return false; // 一方为空 fasle else if (p.val != q.val) return false; // 值不相等 false else return check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left); // 递归检查对称性 } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21广度优先搜索
/** * 广度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution2 { public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return true; else if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return true; else if (root.left == null || root.right == null) return false; Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>(); deque.addFirst(root.left); deque.addLast(root.right); while (!deque.isEmpty()) { Deque<TreeNode> nextDeque = new LinkedList<>(); // 存放下一层的节点 int currentLevelSize = deque.size(); for (int i = 0; i < currentLevelSize; i = i + 2) { // 每次出队首位两个,进行对比 TreeNode p = deque.removeFirst(); TreeNode q = deque.removeLast(); // 检查值是否对称 if (p.val != q.val) return false; // 检查 p、q 的子节点 null 是否对称 if (p.left == null ^ q.right == null || p.right == null ^ q.left == null) return false; // 存放下一层节点 if (p.left != null) { nextDeque.addFirst(p.left); nextDeque.addLast(q.right); } if (p.right != null) { nextDeque.addFirst(p.right); nextDeque.addLast(q.left); } } deque = nextDeque; } return true; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数 (opens new window)中等
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点
root,求出该树的节点个数。完全二叉树 (opens new window) 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第
h层,则该层包含1~ 2h个节点。**进阶:**遍历树来统计节点是一种时间复杂度为
O(n)的简单解决方案。你可以设计一个更快的算法吗?
/**
* 判断左右子树是否满二叉树,直接计算满子树,递归计算不满的子树
* 时间复杂度: O((logN)^2)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
// 计算左右子树高度
int depth1 = depth(root.left);
int depth2 = depth(root.right);
// 左右子树节点个数
int count1, count2;
// 如果左右子树高度相等,则左子树一定是满二叉树,可直接计算左子树个数,递归计算右子树
// 否则,右子树是满二叉树,直接计算右子树个数,递归计算左子树
if (depth1 == depth2) {
count1 = (1 << depth1) - 1; // 左子树满
count2 = countNodes(root.right);
} else {
count1 = countNodes(root.left);
count2 = (1 << depth2) - 1; // 右子树满
}
// 左右子树节点个数 + 根节点 1 个
return count1 + count2 + 1;
}
// 计算二叉树的高度,即统计左链节点个数
private int depth(TreeNode root) {
int depth = 0;
while (root != null) {
root = root.left;
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
平衡二叉树:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
# 注意递归的终止条件(路径总和)
# 问题分析
对于递归函数很重要的一点就是找到递归终止条件,这里看一个终止条件稍微复杂的题目。
112. 路径总和 (opens new window)简单
给你二叉树的根节点
root和一个表示目标和的整数targetSum,判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和targetSum。
深度优先遍历(递归)
这道题适用递归的思想很简单,递归结构为在根节点
root中查找左右孩子查找是否有sum - root.val的路径。/** * 递归 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(h),最坏链条 O(n),平均 O(logn) */ class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null) return false; // 判断是不是叶子节点 if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { return targetSum == root.val; } else { return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18广度优先遍历
/** * 广度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null) return false; Queue<TreeNode> queNode = new LinkedList<>(); // 存节点 Queue<Integer> queVal = new LinkedList<>(); // 存到对应节点经过的路径和 queNode.offer(root); queVal.offer(root.val); while (!queNode.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queNode.poll(); // 达到的节点 int value = queVal.poll(); // 到达该节点经过的路径和 // 如果到叶子节点了,判断经过的路径和 if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { if (value == targetSum) return true; continue; } // 没到达叶子节点,存入子节点,和到达子节点经过的路径和 if (node.left != null) { queNode.offer(node.left); queVal.offer(value + node.left.val); } if (node.right != null) { queNode.offer(node.right); queVal.offer(value + node.right.val); } } return false; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 相关题目
404. 左叶子之和 (opens new window)简单
计算给定二叉树的所有左叶子之和。
深度优先遍历
/** * 深度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; int res = 0; // 如果左子树的叶子节点,加上 value,否则加上左子树中左边叶节点的和 res += isLeafNode(root.left) ? root.left.val : sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left); // 如果右子树是叶子节点,不用加,否则加上右子树中左边叶节点的和 res += isLeafNode(root.right) ? 0 : sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right); return res; } // 判断是不是叶子节点 private boolean isLeafNode(TreeNode node) { return node != null && node.left == null && node.right == null; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22广度优先遍历
/** * 广度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; int res = 0; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); // 考察左子树,如果是叶子节点,累计 value,否则入队待考察 if (node.left != null) { if (isLeafNode(node.left)) { res += node.left.val; } else { queue.offer(node.left); } } // 考察右子树,只有不是叶子节点的时候才入队待考察 if (node.right != null && !isLeafNode(node.right)) { queue.offer(node.right); } } return res; } // 判断是不是叶子节点 private boolean isLeafNode(TreeNode node) { return node.left == null && node.right == null; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# 定义递归问题(二叉树的所有路径)
前面递归相关题目的逻辑部分都很简单,这一节来看一下逻辑略微复杂一些的题目。在这个问题中大家也可以体会下如何利用递归函数的返回值。
257. 二叉树的所有路径 (opens new window)简单
给你一个二叉树的根节点
root,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
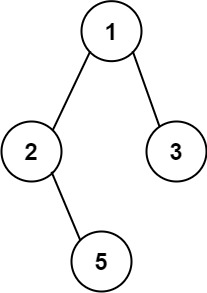
**输入:**root = [1, 2, 3, null, 5] 输出:["1->2->5", "1->3"]
这个问题的递归结构也很简单,我们要找从 root 出发的所有路径,只需要找到左右子树的所有路径,然后前面加上 root.val-> ,并合并两组路径即可。这里我们要注意递归终止条件是到达了叶子节点就返回路径,递归的返回值是 路径数组。
深度优先遍历(递归)
这道题适用递归的思想很简单,递归结构为在根节点
root中查找左右孩子查找是否有sum - root.val的路径。/** * 深优先限遍历(递归) * 时间复杂度: O(n), n为树中的节点个数 * 空间复杂度: O(h), h为树的高度 */ class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) { // 存放从本节点 root,到所有叶子节点的路径 List<String> paths = new ArrayList<>(); // 如果是 null,递归结束 if (root == null) return paths; // 如果是叶子节点,递归结束 if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { paths.add(String.valueOf(root.val)); return paths; } // 获取左孩子到叶子节点的所有路径 List<String> leftPaths = binaryTreePaths(root.left); // 获取右孩子到所有叶子节点的路径 List<String> rightPaths = binaryTreePaths(root.right); // 左右孩子的路径前面加上 root,就是 root 到所有叶子节点的路径 for (String leftPath : leftPaths) paths.add(root.val + "->" + leftPath); for (String rightPath : rightPaths) paths.add(root.val + "->" + rightPath); return paths; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32广度优先遍历
/** * 广度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution2 { public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) { List<String> paths = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) return paths; Queue<TreeNode> queNode = new LinkedList<>(); Queue<String> quePath = new LinkedList<>(); queNode.offer(root); quePath.offer(String.valueOf(root.val)); while (!queNode.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queNode.poll(); String path = quePath.poll(); if (node.left == null && node.right == null) paths.add(path); if (node.left != null) { queNode.offer(node.left); quePath.offer(path + "->" + node.left.val); } if (node.right != null) { queNode.offer(node.right); quePath.offer(path + "->" + node.right.val); } } return paths; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 相关问题
113. 路径总和 II (opens new window)中等
给你二叉树的根节点
root和一个整数目标和targetSum,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]1
2
深度优先遍历
/** * 深度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(h) */ class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) return paths; // 如果是子节点 if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.val == targetSum) { List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); path.add(root.val); paths.add(path); } return paths; } // 左子树路径 List<List<Integer>> leftPaths = pathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val); // 右子树路径 List<List<Integer>> rightPaths = pathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val); // 左右子树路径合并 for (List<Integer> leftPath : leftPaths) { leftPath.add(0, root.val); paths.add(leftPath); } for (List<Integer> rightPath : rightPaths) { rightPath.add(0, root.val); paths.add(rightPath); } return paths; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37广度优先遍历
/** * 广度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) return paths; Queue<TreeNode> queNode = new LinkedList<>(); Queue<List<Integer>> quePath = new LinkedList<>(); Queue<Integer> queSum = new LinkedList<>(); queNode.offer(root); quePath.offer(new LinkedList<Integer>() {{ add(root.val); }}); queSum.offer(root.val); while (!queNode.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queNode.poll(); List<Integer> path = quePath.poll(); Integer sum = queSum.poll(); // 如果到了子节点 if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { if (sum == targetSum) paths.add(path); continue; } // 如果左右有孩子,入队 if (node.left != null) { queNode.offer(node.left); List<Integer> nextPath = new LinkedList<>(path); // path 要复制一份 nextPath.add(node.left.val); quePath.offer(nextPath); queSum.offer(sum + node.left.val); } if (node.right != null) { queNode.offer(node.right); List<Integer> nextPath = new LinkedList<>(path); // path 要复制一份 nextPath.add(node.right.val); quePath.offer(nextPath); queSum.offer(sum + node.right.val); } } return paths; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和 (opens new window)中等
给你一个二叉树的根节点
root,树中每个节点都存放有一个0到9之间的数字。每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
- 例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径
1 -> 2 -> 3表示数字123。计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和 。
输入:root = [1,2,3] 输出:251
2
深度优先遍历
/** * 深度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(h) */ class Solution { public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) { return dfs(root, 0); } private int dfs(TreeNode root, int sum) { if (root == null) { return 0; } sum = sum * 10 + root.val; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { return sum; } else { return dfs(root.left, sum) + dfs(root.right, sum); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22广度优先遍历
/** * 广度优先遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; int sum = 0; Queue<TreeNode> queNode = new LinkedList<>(); Queue<Integer> queSum = new LinkedList<>(); queNode.offer(root); queSum.offer(root.val); while (!queNode.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queNode.poll(); Integer currSum = queSum.poll(); if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { sum += currSum; continue; } if (node.left != null) { queNode.offer(node.left); queSum.offer(currSum * 10 + node.left.val); } if (node.right != null) { queNode.offer(node.right); queSum.offer(currSum * 10 + node.right.val); } } return sum; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 复杂的递归逻辑(路径总和 III)
437. 路径总和 III (opens new window)中等
给定一个二叉树的根节点
root,和一个整数targetSum,求该二叉树里节点值之和等于targetSum的 路径 的数目。路径 不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
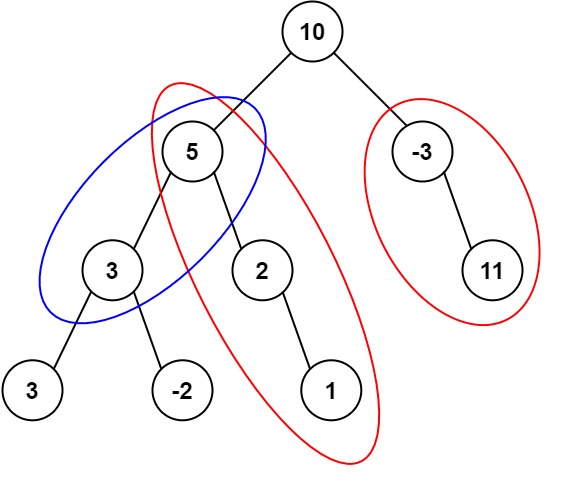
输入:root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8 输出:3 解释:和等于 8 的路径有 3 条,如图所示。1
2
3
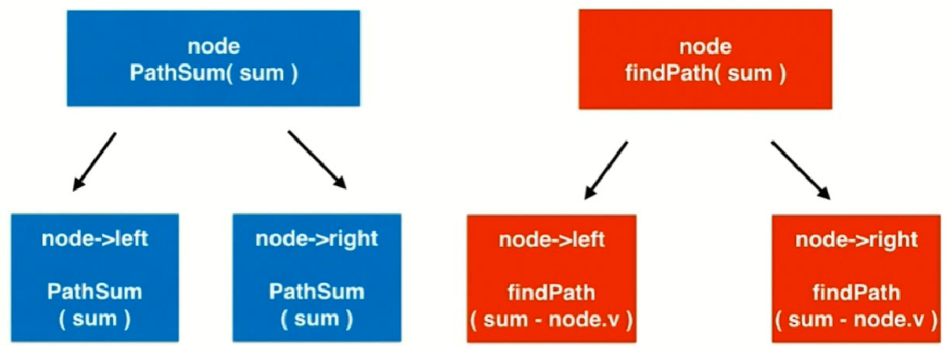
之前递归求节点路径的时候,默认当前根节点在路径上,然后在左右孩子中找和为 targetSum-root.val 的路径。本题递归有两种情况,一种当前节点在路径上,和上述过程一样;一种当前节点不在路径上,在左右孩子中找和为 targetSum 的路径。如下图所示。
/**
* 双递归
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
* 空间复杂度: O(h)
*/
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
// 包含当前节点的结果
int res = findPath(root, targetSum);
// 不包含当前节点的结果
res += pathSum(root.left, targetSum) + pathSum(root.right, targetSum);
return res;
}
/**
* 在 root 为跟的二叉树中,寻找包含 root 的路径,和为 sum
* @param root 二叉树根节点
* @param targetSum 路径和
* @return 返回这样的路径个数
*/
private int findPath(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
int res = 0;
if (targetSum == root.val)
res += 1;
res += findPath(root.left, targetSum - root.val);
res += findPath(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
由于没有规定路径一定要到叶子节点,并且节点值可能有负数,所以逻辑上比之前的 112. 路径总和 (opens new window) 和 113. 路径总和 II (opens new window) 复杂不少,不过思路大致相同。
# 二分搜索树中的问题(二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先)
二分搜索树:每个节点的键值大于左孩子;每个节点的键值小于右孩子;以左右孩子为根的子树仍为二分搜索树。
二分搜索树是二叉树的一种,请大家复习二分搜索树的基本操作:
- 插入 insert
- 查找 find
- 删除 delete
- 最大值,最小值 minimum, maximum
- 前驱,后继 successor,predecessor
- 上界,下界 floor,ceil
- 某个元素的排名 rank
- 寻找第 k 大(小)元素 select
由于二分搜索树的结构特点,以上操作的时间复杂度都是 O(logN) 的。
# 问题分析
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 (opens new window)简单
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
最近公共祖先的定义为:对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。
对于根节点 root,我们可以分析输出以下递归结构:
- 如果 p 和 q 都小于 root,则去 root 的左侧找它们的最近公共祖先
- 如果 p 和 q 都大于 root,则去 root 的右侧找它们的最近公共祖先
- 如果 p 和 q 在 root 的两边,则 root 就是它们的最近公共祖先
- 如果 p 和 q 其中之一等于 root,那它就是最近公共祖先
递归
/** * 递归 * 时间复杂度: O(logN) * 空间复杂度: O(h) */ class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { // 如果 p、q 落在一侧,继续向下递归 if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) { return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); } else if (p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) { return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); } else { // 递归结束条件, p、q 不在一侧,此时 root 就是最近公共祖先 return root; } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18迭代,两次查找
/** * 迭代,两次查找 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { // 获得 root 到 p、q 的路径 List<TreeNode> path_p = getPath(root, p); List<TreeNode> path_q = getPath(root, q); // 对比两条路径,找到最后一个相同的节点 TreeNode ancestor = null; int step = Math.min(path_p.size(), path_q.size()); for (int i = 0; i < step; i++) { if (path_p.get(i) == path_q.get(i)) { ancestor = path_p.get(i); } else { break; } } return ancestor; } // 找出从根节 root 点到节点 target 的路径 private List<TreeNode> getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode target) { List<TreeNode> path = new ArrayList<>(); TreeNode node = root; while (node != target) { path.add(node); if (target.val < node.val) node = node.left; else node = node.right; } path.add(node); return path; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38迭代,一次查找
/** * 迭代,一次查找 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) */ class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { // 查找第一个分岔点 while (true) { // 如果 p、q 落在同侧子树,说明没分岔,继续向下查找;否则循环结束 if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) { root = root.left; } else if (p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) { root = root.right; } else { break; } } return root; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 相关问题
98. 验证二叉搜索树 (opens new window)中等
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
递归,区间判断
/** * 递归,区间判断 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE); } // 验证二叉搜索树,root 的值必须在 (lower, upper) 开区间内 private boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, long lower, long upper) { if (root == null) { return true; } if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) { return false; } return isValidBST(root.left, lower, root.val) && isValidBST(root.right, root.val, upper); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21中序遍历,利用中序遍历是排好序的特点
/** * 中序遍历 * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(n) */ class Solution { // 利用二分搜索树的中序遍历是顺序的特性 public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return true; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); long preVal = Long.MIN_VALUE; while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { // 1、左链入栈 while (root != null) { stack.push(root); root = root.left; } // 2、出栈一个 TreeNode node = stack.pop(); // -- 遍历时机 -- if (node.val <= preVal) { return false; } preVal = node.val; // 3、变换 root root = node.right; } return true; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 (opens new window)中等
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
- 首先找到需要删除的节点;
- 如果找到了,删除它。
说明: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O(h),h 为树的高度。
前驱法
/** * 前驱法 * 时间复杂度: O(logN) * 空间复杂度: O(H) */ class Solution { public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) { if (root == null) return root; if (key == root.val) { // (1) 删除 root if (root.left == null) return root.right; if (root.right == null) return root.left; // 找 root 的前驱节点 predecessor TreeNode predecessor = root.left; while (predecessor.right != null) { predecessor = predecessor.right; } // 方式一:右边子树接到 predecessor 右孩子位置(相对不平衡) // predecessor.right = root.right; // return root.left; // 方式二:predecessor 替换 root,删除原 predecessor(相对平衡) root.val = predecessor.val; root.left = deleteNode(root.left, predecessor.val); return root; } else if (key < root.val) { // (2) 去左子树删除 root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key); return root; } else { // (3) 去右子树删除 root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key); return root; } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33后继法
/** * 后继法 * 时间复杂度: O(logN) * 空间复杂度: O(H) */ class Solution { public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) { if (root == null) return root; if (key == root.val) { // (1) 删除 root if (root.left == null) return root.right; if (root.right == null) return root.left; // 找 root 的后继节点 successor TreeNode successor = root.right; while (successor.left != null) { successor = successor.left; } // 方式一:左边子树接到 successor 左孩子位置(相对不平衡) // successor.left = root.left; // return root.right; // 方式二:successor 替换 root,删除原 successor(相对平衡) root.val = successor.val; root.right = deleteNode(root.right, successor.val); return root; } else if (key < root.val) { // (2) 去左子树删除 root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key); return root; } else { // (3) 去右子树删除 root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key); return root; } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 (opens new window)简单
给你一个整数数组
nums,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 高度平衡 二叉搜索树。高度平衡 二叉树是一棵满足「每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 」的二叉树。
/**
* 中序遍历特点,选取区间中点作为根节点
* 时间复杂度: O(N)
* 空间复杂度: O(logN)
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return sortedArrayToBST(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
/**
* 将有序数组 nums[l...r] 区间转换为二叉搜索树
*/
private TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if (l > r) return null;
if (l == r) return new TreeNode(nums[l]);
// 选取中点作为根节点
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = sortedArrayToBST(nums, l, mid - 1);
root.right = sortedArrayToBST(nums, mid + 1, r);
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素 (opens new window)中等
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点
root,和一个整数k,请你设计一个算法查找其中第k个最小元素(从 1 开始计数)。
根据左子树节点个数查找
/** * 根据子树节点个数查找 */ class Solution { public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) { // 计算 root 的左子树节点个数 count_l int count_l = nodeCount(root.left); if (count_l == k - 1) { // 此时 root 就是第 k 小的节点 return root.val; } else if (count_l > k - 1) { // 左子树不止 k 个节点,root 大于第 k 小节点,去左子树中找 return kthSmallest(root.left, k); } else { // 左子树个数不足 k-1 个,root 小于第 k 小节点,去右子树找 return kthSmallest(root.right, k - count_l - 1); } } // 返回二叉搜索树 root 的节点个数 private int nodeCount(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; return nodeCount(root.left) + nodeCount(root.right) + 1; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23中序遍历排序(递归)
/** * 中序遍历排序,递归法 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(N) */ class Solution { public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) { List<Integer> list = inOrder(root, new ArrayList<>()); return list.get(k - 1); } private List<Integer> inOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) { if (root == null) return list; inOrder(root.left, list); list.add(root.val); inOrder(root.right, list); return list; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19中序遍历排序(迭代)
/** * 中序遍历排序,迭代法 * 时间复杂度: O(H + k) * 空间复杂度: O(H + k) */ class Solution { public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); while (true) { while (root != null) { stack.push(root); root = root.left; } root = stack.pop(); if (--k == 0) return root.val; root = root.right; } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 (opens new window)中等
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
最近公共祖先:对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。
获得根节点到目标节点的路径,对比路径
/** * 获得根节点到目标节点的路径,对比路径 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(N) */ class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { // 查找 LinkedList<TreeNode> path_p = findPath(root, p, new LinkedList<>()); LinkedList<TreeNode> path_q =findPath(root, q, new LinkedList<>()); TreeNode parent = null; while (true) { if (path_p.isEmpty() || path_q.isEmpty()) break; TreeNode node_p = path_p.remove(); TreeNode node_q = path_q.remove(); if (node_p != node_q) break; else parent = node_p; } return parent; } // 查找从 root 到 node 的路径,拼到 path 中 private LinkedList<TreeNode> findPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode node, LinkedList<TreeNode> path) { if (root == node) { path.addFirst(node); return path; } if (path.size() == 0 && root.left != null) findPath(root.left, node, path); if (path.size() == 0 && root.right != null) findPath(root.right, node, path); if (path.size() > 0) path.addFirst(root); return path; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43判断节点在子树的分布
/** * 判断节点在子树的分布 * 时间复杂度: O(N) * 空间复杂度: O(N) */ class Solution { // 存放最近公共祖先 private TreeNode res; public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { res = null; this.contains(root, p, q); return res; } /** * 返回二叉树 root 中是否包含 p 或 q * * @return 包含其中 p 或 q 其中一个就返回 true */ private boolean contains(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null) return false; boolean l = contains(root.left, p, q); // 左子树是否包含 boolean r = contains(root.right, p, q); // 右子树是否包含 // 如果左右子树都包含,说明一边一个,root 为最近公共祖先 if (l && r) res = root; // 如果根节点包含,另一个在子树中包含,root 为最近公共祖先 if ((p.val == root.val || q.val == root.val) && (l || r)) res = root; // 左边包含 || 右边包含 || 根节点包含 return l || r || (p.val == root.val || q.val == root.val); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37